| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- spring security 설정
- 혼공얄코
- 입출력
- spring security
- 오버로딩
- StringBuffer
- LocalDate
- 오블완
- 둘만의 암호 자바
- 프로그래머스
- hackerrank
- 캡슐화
- 자바의정석
- CPU
- 자바의 정석
- 리눅스
- 다형성
- BFS
- java
- 프로그래머스 둘만의 암호
- 멀티태스킹
- 오버라이딩
- 티스토리챌린지
- SQL Mapper
- 멀티프로세싱
- 백트래킹
- localtime
- StringBuilder
- 둘만의 암호
- over()
- Today
- Total
쉽게 쉽게
날짜와 시간 본문
이 글은 '자바의 정석'의 내용을 기반으로 공부한 내용을 덧붙인 글입니다.
1. java.time 패키지
JDK1.8이전에는 Date와 Calendar를 사용했지만, 1.8이후에는 java.time패키지가 추가되었다.
★ Calendar와 차이점
java.time패키지가 가진 클래스들은 '불변'하다는 특징을 가지고 있다.
그래서 날짜나 시간을 변경하는 메서드들은 기존의 객체를 변경하는 대신 항상 변경된 새로운 객체를 반환한다.
기존 Calendar는 변경가능하므로, *멀티쓰레드 환경에서 안전하지 못하다.
멀티쓰레드 환경이란
멀티쓰레드 환경에서는 동시에 여러 쓰레드가 같은 객체에 접근할 수 있기 때문에 변경 가능한 객체는 데이터가 잘못될 가능성이 있으므로 이를 쓰레드에 안전하지 않다고 한다.
2. 핵심 클래스
(1) LocalDate 날짜 클래스 , LocalTime 시간 클래스
★ 공통메서드
현재의 날짜와 시간을 반환하는 now()
지정된 날짜와 시간으로 객체를 생성하는 of()
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now(); // 오늘 날짜
LocalTime now = LocalTime.now(); // 현재 시간
LocalDate birthday = LocalDate.of(1999, 12, 31) // 1999년 12월 31일
LocalTime birthTime = LocalTime.of(23, 59, 59) // 23시 59분 59초LocalDate 메서드

주의할 점은
Calendar는 월의 범위가 0부터 시작
11이 12월을 의미 (0이 1월...)
요일은 일요일부터 1 (월요일 2...)
LocalDate는 월의 범위가 1부터 시작
12는 12월 (1이 1월...),
요일은 월요일이 1 이다. (화요일 2...)
LocalTime 메서드

(2) TemporalField과 TemporalUnit 인터페이스
★ TemporalField
년, 월, 일 등 날짜와 시간의 필드를 정의해 놓은 것으로, 열거형 ChronoField가 이 인터페이스를 구현했다.
날짜와 시간에서 특정 필드의 값만을 얻을 때는 get()이나, get으로 시작하는 이름의 메서드를 사용한다.
이 때 정의되어 있는 ChronoField를 사용하면 편리하게 값을 얻을 수 있다.
LocalTime now = LocalTime.now(); // 현재 시간
int minute = now.getMinute(); // 현재 시간에서 분만 알아낸다.
int minute = now.get(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR) // 위의 문장과 동일하다.아래는 매개변수로 사용할 수 있는 목록들이다.
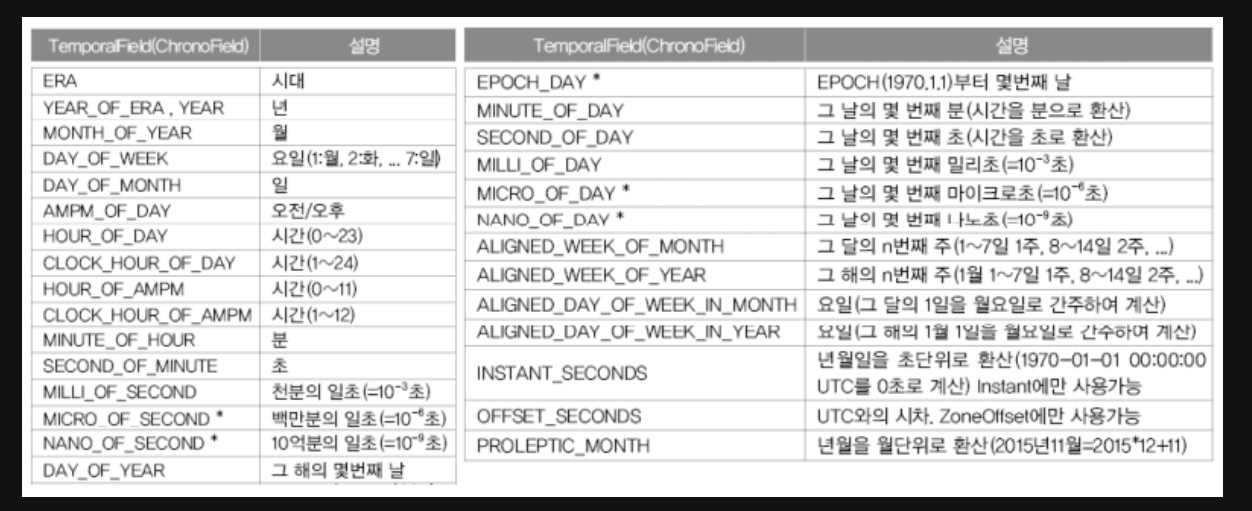
단 주의할 점은 LocalDate는 날짜를 표시하기 위한 것이므로, 시간에 대한 변수를 사용하면 오류가 발생한다.
반대로 LocalTime에 날짜 변수가 오는 것도 오류가 발생한다.
★ TemporalUnit
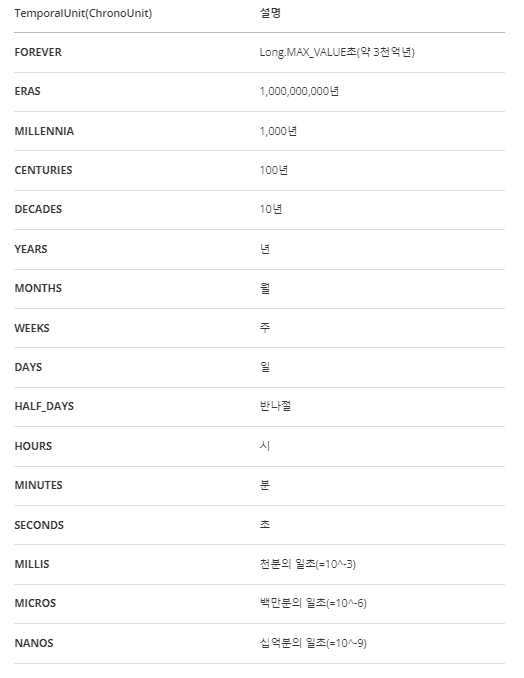
날짜와 시간의 단위를 정의해 놓은 것이 TemporalUnit인터페이스이며, 이 인터페이스를 구현한 것이 ChronoUnit이다.
특정 날짜와 시간에서 지정된 단위의 값을 더하거나 뺄 때는 plus()나 minus()메서드를 사용한다.
이 때 ChronoUnit을 사용하면 편리하게 값을 구할 수 있다.
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now(); // 오늘
LocalDate tomorrow = today.plus(1); // 오늘에 1일을 더한다.
LocalDate tomorrow = today.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS); // 위와 동일하다.아래는 매개변수로 사용할 수 있는 목록들이다.
★ 필드의 값 변경하기
LocalDate with(TemporalField field, long new value) // 날짜를 변경하는 메서드
LocalTime with(TemporalField field, long new value) // 시간을 변경하는 메서드
위에있는 TemporalField의 값이 매개변수로 들어갈 수 있다.
★ 사용가능한 메서드
withYear(int year)
withMonth(int month)
withDayOfMonth(int dayOfMonth)
withDayOfYear(int dayOfYear)
...
withHour(int hour)
withMinute(int minute)
withSecond(int second)
withNano(int nanoOfSecond)
...LocalDate date = LocalDate.now(); // 오늘 날짜
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now(); // 오늘 시간
date = date.withYear(2023); // 년도를 2023년으로 변경
time = time.withHour(12); // 시간을 12시로 변경주의할 점은 필드를 변경하는 메서드들은 항상 새로운 객체를 생성해서 반환하므로 대입 연산자(=)를 같이 사용해야 한다는 것이다.
★ 값을 더하거나 빼는 메서드
LocalTime plus(TemporalAmonut amountToAdd)
LocalTime plus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)
LocalDate plus(TemporalAmonut amountToAdd)
LocalDate plus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)위에있는 TemporalUnit의 값이 매개변수로 들어갈 수 있다.
plus()와 minus()
date = date.plusYears(1);
date = date.plusMonths(1);
date = date.plusDays(1);
date = date.plusWeeks(1);
time = time.plusHours(1);
time = time.plusMinutes(1);
time = time.plusSeconds(1);
time = time.plusNanos(1);minus()는 plus부분을 minus로 바꾸기만 하면 된다.
그러나 plus()와 minus()를 사용해서 변경하기에는 불편한 것이 있다.
그래서 자주 쓰일만한 날짜 계산들을 도와주는 메서드를 정의해 놓은 것이 TemporalAdjseters클래스이다.
★ TemporalAdjseters 메서드
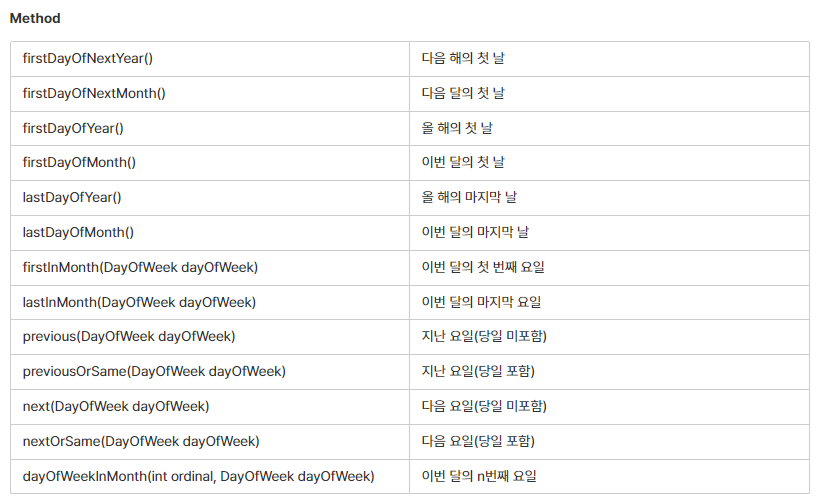
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate nextMonday = today.with(TemporalAdjusters.next(DayOfWeek.MONDAY)); //다음주 월요일★ LocalTime에만 있는 메서드
truncatedTo() 지정된 것보다 작은 단위의 필드를 0으로 만든다.
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now(); // 오늘 시간
time = time.truncatedTo(ChronoUnit.HOURS); //시(hours)보다 작은 단위를 0으로 만든다.단 LocalDate의 필드인 날짜는 0이 될 수 없기 때문에 사용할 수 없다.
시간에 관련된 매개변수만 들어갈 수 있다.
★ 날짜와 시간의 비교
LocalDate와 LocalTime도 compareTo()가 적절히 오버라이딩 되어있어서 이를 이용해 비교를 할 수 있다.
그러나 보다 편리하게 비교하기 위한 메서드들이 있다.
boolean isAfter(ChronoLocalDate other)
boolean isBefore(ChronoLocalDate other)
boolean isEqual(ChronoLocalDate other) // LocalDate에만 있음 LocalDate date = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.now();
date = date.withYear(2023); // 년도를 2023년으로 변경
date2 = date2.withYear(2024); // 년도를 2024년으로 변경
System.out.println(date.isAfter(date2));//false
System.out.println(date.isBefore(date2));//true
System.out.println(date.isEqual(date2));//false단 isAfter와 isBefore는 같은 날짜면 false 반환
(3) LocalDateTime 날짜와 시간
LocalDate와 LocalTime를 합쳐서 LocalDateTime을 만들 수 있다.
LocalDate date = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now();
//LocalDateTime으로 만드는 방법
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2023, 12, 31, 12, 30, 30);
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.of(date, time);
LocalDateTime dt2 = date.atTime(time);
LocalDateTime dt3 = date.atTime(12,30,30);
LocalDateTime dt4 = date.atStartOfDay(); // date.atTime(0,0,0)''
LocalDateTime dt5 = time.atDate(date);
LocalDateTime dt6 = time.atDate(LocalDate.of(2023,5,5));반대로 LocalDateTime을 LocalDate 또는 LocalTime으로 변환할 수 있다.
LocalDate date2 = dateTime.toLocalDate();
LocalTime time2 = dateTime.toLocalTime();(4) Period와 Duration
Period는 날짜의 차이를, Duration는 시간의 차이를 계산한다.
날짜 - 날짜 = Period
시간 - 시간 = Duration
★ Period는 between()으로 날짜의 차이를 구한다.
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2023, 1, 29);
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.of(2024, 12, 30);
Period pe = Period.between(date1, date2);
System.out.println(pe.get(ChronoUnit.MONTHS)); // 11
System.out.println(pe.get(ChronoUnit.YEARS)); // 1
LocalTime time1 = LocalTime.of(00, 00, 00);
LocalTime time2 = LocalTime.of(12, 30, 30);
Duration du = Duration.between(time1, time2);
System.out.println(du.get(ChronoUnit.SECONDS)); // 45030
System.out.println(du.get(ChronoUnit.NANOS)); // 0Period와 Duration에서 특정 필드의 값을 얻을 때는 get()을 사용한다.
이때, Duration에는 getHours(), getMinutes() 같은 메서드가 없다.
때문에 Duration를 LocalTime으로 변환한 다음에, LocalTime의 get 메서드를 사용하는게 편리하다.
Duration du = Duration.between(time1, time2);
LocalTime tmpTime = LocalTime.of(0,0).plusSeconds(du.getSeconds());
int hours = tmpTime.getHour();
int min = tmpTime.getMinute();
int sec = tmpTime.getSecond();
int nano = du.getNano();(5) DateTimeFormatter
날짜와 시간을 원하는 형식으로 출력하고 해석해주는 클래스
format() 메서드는 LocalDate나 LocalTime에도 정의되어 같은 기능을 한다.(편리한 쪽을 사용하면 된다.)
LocalDate date = LocalDate.now();
String yyyymmdd1 = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE.format(date);
System.out.println(yyyymmdd1); // 2023-01-29
String yyyymmdd2 = date.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE);
System.out.println(yyyymmdd2); // 2023-01-29아래는 DateTimeFormatter에 상수로 정의된 형식들의 목록이다.
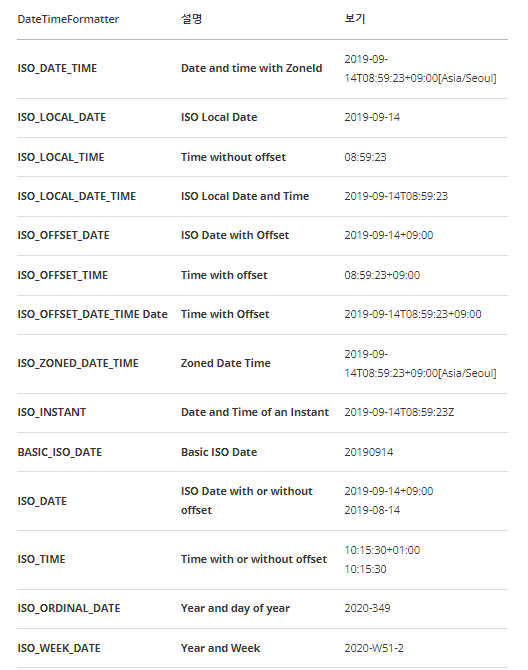
★ DateTimeFormatter의 static메서드 ofLocalizedDate(), ofLocalizedTime(), ofLocalizedDateTime()
미리 정의되어있는 형식이라고 보면 된다.
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDate(FormatStyle.SHORT);
String shortFormat = formatter.format(LocalDate.now());
System.out.println(formatter); //Localized(SHORT,)
System.out.println(shortFormat); // 23. 1. 29.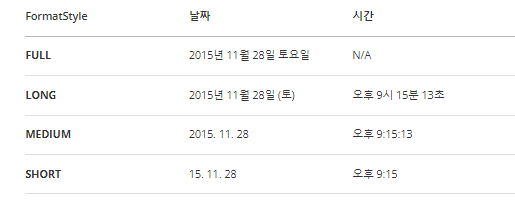
★ 출력형식 직접 정의하기
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/mm/dd");ofPattern으로 원하는 출력형식을 직접 작성할 수 있다.
아래는 자주 사용하는 출력형식 목록이다.
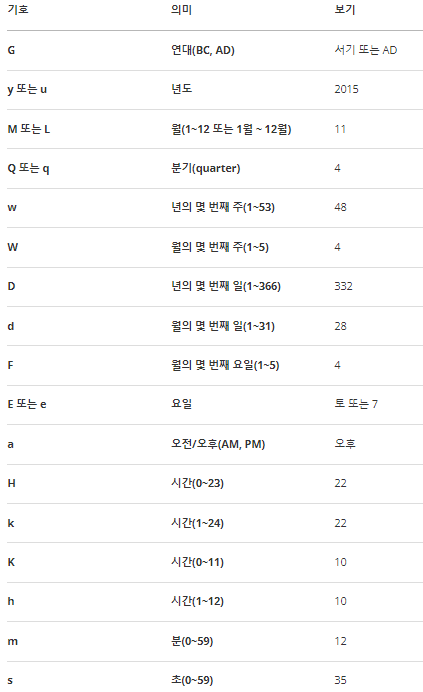
(6) 문자열을 날짜와 시간으로 변환하기
문자열을 날짜와 시간으로 변환하려면 parse() 메서드를 이용하면 된다.
날짜와 시간을 표현하는데 사용되는 클래스에는 이 메서드가 거의 다 포함되어 있다.
static LocalDateTime parse(CharSequence text) // 기본적인 파싱 메서드
static LocalDateTime parse(CharSequence text, DateTimeFormatter formatter) // 상수로 정의된 형식으로 변환할때 사용하는 메서드
LocalDate newDate = LocalDate.parse("2023-01-23");
LocalTime newTime = LocalTime.parse("23:59:59");
LocalDate newDate2 = LocalDate.parse("2023-01-23", DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE);
DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime endOfYear = LocalDateTime.parse("2023-12-31 23:59:59", pattern);| 잘못된 내용이 있다면 지적부탁드립니다. 방문해주셔서 감사합니다. |

'Java > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Arrays와 Collections (1) | 2023.03.24 |
|---|---|
| 컬렉션 프레임웍 (0) | 2023.03.23 |
| Java.lang 패키지 (1) | 2023.03.21 |
| 예외처리 (0) | 2023.03.20 |
| 인터페이스 (0) | 2023.03.20 |





